如果我们有想固定间隔时间执行的任务等,自己实现的一种方式是可以新启动一个线程,在其中sleep固定的时间后执行,但是这种方式在任务多的时候肯定是不行的。现在已经有很多现成的工具我们可以直接使用,这里主要介绍一下JDK的ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor与Netty的HashedWheelTimer,看一下它们的实现原理
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor是JDK自带的一个用于执行周期任务的线程池,用法大致如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(5);
executor.schedule(() -> System.out.println("111"), 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> System.out.println("22"), 2, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> System.out.println("33"), 1, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
了解它原理话需要先了解一下线程池的使用,线程池中是多个线程从一个阻塞队列中获取任务来进行执行
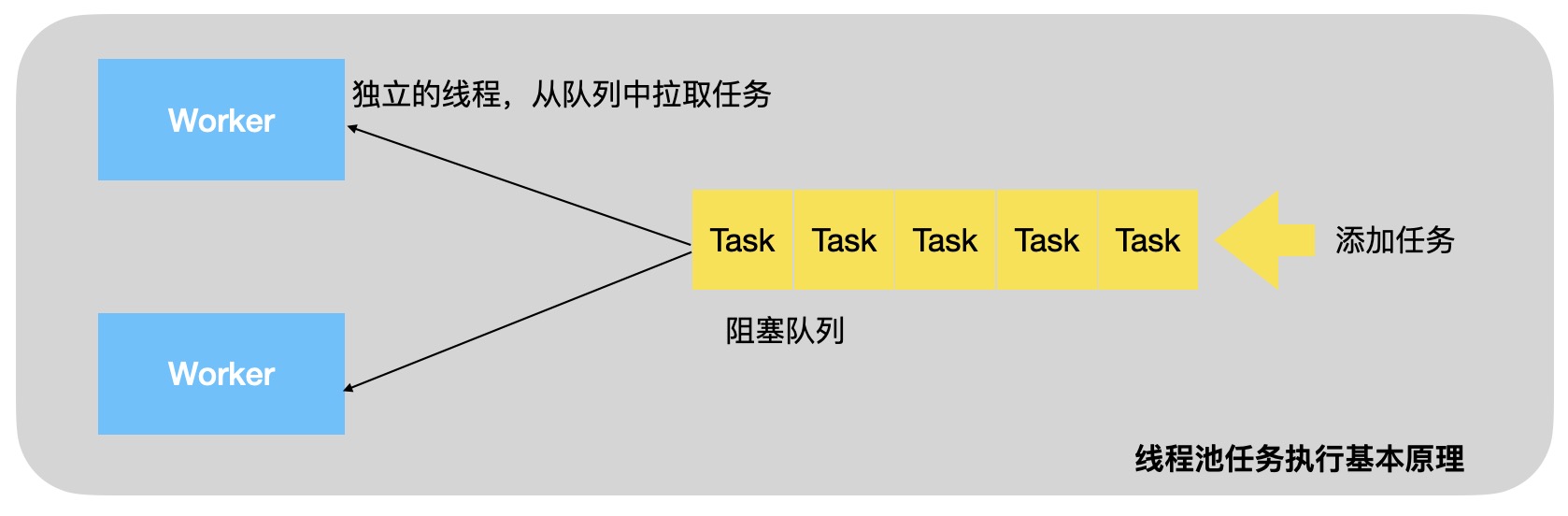
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor是继承了ThreadPoolExecutor,其中最大的一个区别是提供了一个延迟工作队列DelayedWorkQueue,内部是一个优先级队列,需要最先执行的排在最前面,每次插入数据的时候会重新排序
同时还实现了ScheduledFutureTask任务类,其中除了记录原始任务外还会记录任务要执行的时间等信息
这样每次拿到任务的时候都是需要最先执行的,判断下如果到达了执行时间就可以执行
HashedWheelTimer
使用ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor最大的一个问题是每次提交任务的时候,都会再次进行一下队列的排序,这个工作时间复杂度为O(nlogn),下面我们看一下HashedWheelTimer的使用例子及实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
HashedWheelTimer timer = new HashedWheelTimer();
Timeout timeout = timer.newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
System.out.println("111");
}
}, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
实现原理如下图所示
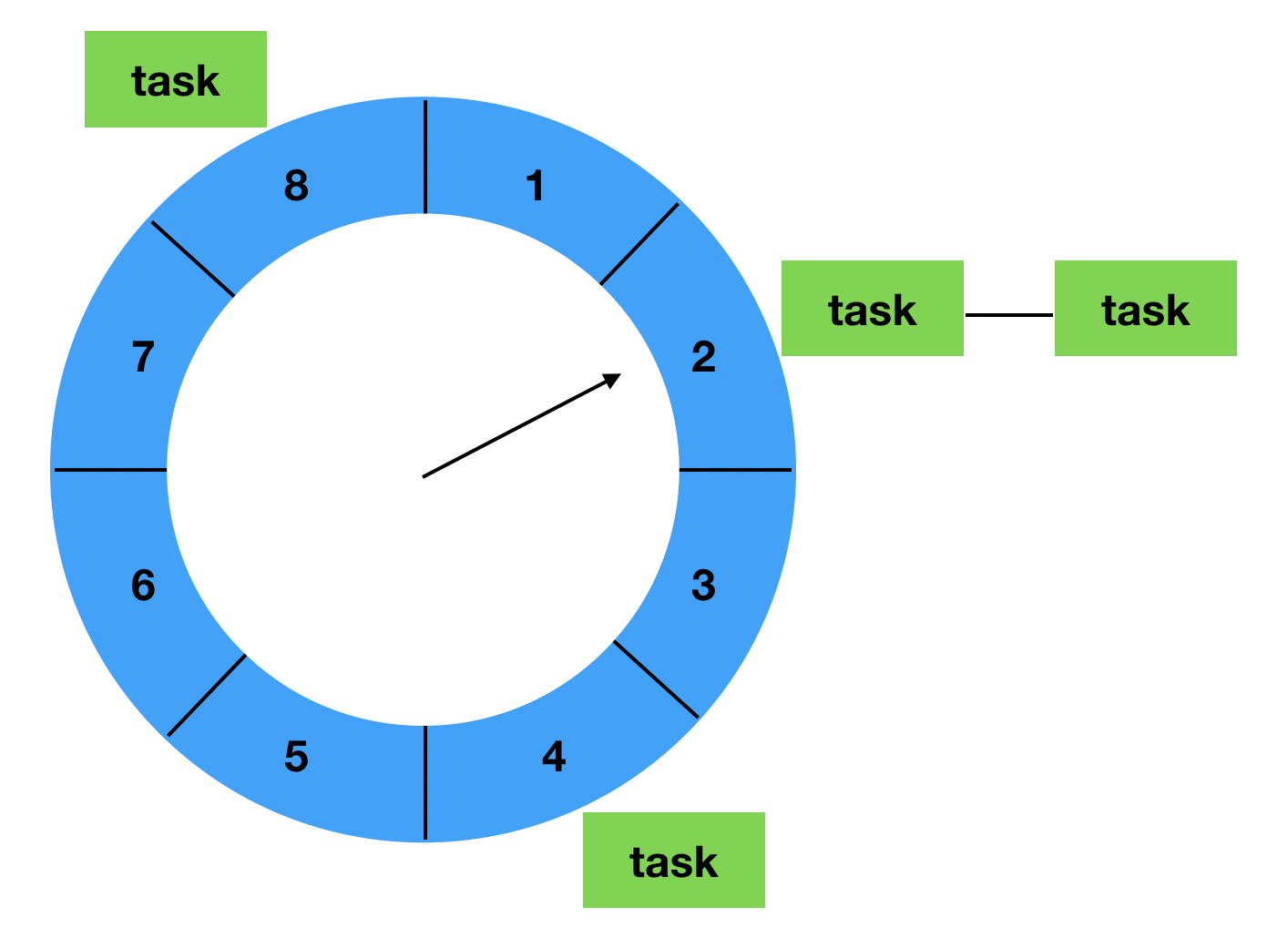
有一个固定长度的数组(时间轮),有一个可以理解为指针,每隔固定时间(tickDuration)会移动到下一个数组索引上,循环往复。当指针到达对应数组元素时,会获取链表中的元素进行遍历,如果任务达到了指定轮次和执行时间就执行,否则减少其中的轮次
每个数组元素有一个定时任务的链表,当有一个定时任务提交时,会根据它距离执行的时间,和任务线程启动的时间,来根据差值计算出任务需要放置到的索引位置(超过一圈的会增加一个轮次),插入到对应的链表中 O(1) 。
下面分析一下对应源码,我们只根据主线看一下最核心的流程,相关代码进行了简化调整
1
2
|
HashedWheelTimer timer = new HashedWheelTimer();
|
看下基础的构造器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public HashedWheelTimer(
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
long tickDuration, TimeUnit unit, int ticksPerWheel, boolean leakDetection,
long maxPendingTimeouts) {
wheel = createWheel(ticksPerWheel);
mask = wheel.length - 1;
long duration = unit.toNanos(tickDuration);
this.tickDuration = duration;
workerThread = threadFactory.newThread(worker);
}
|
之后开始添加任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
| Timeout timeout = timer.newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
System.out.println("111");
}
}, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
进入对应的源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| public Timeout newTimeout(TimerTask task, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
start();
long deadline = System.nanoTime() + unit.toNanos(delay) - startTime;
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = new HashedWheelTimeout(this, task, deadline);
timeouts.add(timeout);
return timeout;
}
public void start() {
switch (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(this)) {
case WORKER_STATE_INIT:
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, WORKER_STATE_INIT, WORKER_STATE_STARTED)) {
workerThread.start();
}
break;
}
while (startTime == 0) {
try {
startTimeInitialized.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ignore) {
}
}
}
|
线程中对应的代码如下(为了便于理解和关注重点,代码已进行简化调整,详情可以查看对应源码)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
| private final class Worker implements Runnable {
public void run() {
startTime = System.nanoTime();
startTimeInitialized.countDown();
do {
final long deadline = waitForNextTick();
if (deadline > 0) {
int idx = (int) (tick & mask);
processCancelledTasks();
HashedWheelBucket bucket = wheel[idx];
transferTimeoutsToBuckets();
bucket.expireTimeouts(deadline);
tick++;
}
} while (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(HashedWheelTimer.this) == WORKER_STATE_STARTED);
}
private long waitForNextTick() {
long deadline = tickDuration * (tick + 1);
for (;;) {
final long currentTime = System.nanoTime() - startTime;
long sleepTimeMs = (deadline - currentTime + 999999) / 1000000;
if (sleepTimeMs <= 0) {
return currentTime;
}
Thread.sleep(sleepTimeMs);
}
}
private void transferTimeoutsToBuckets() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = timeouts.poll();
long calculated = timeout.deadline / tickDuration;
timeout.remainingRounds = (calculated - tick) / wheel.length;
final long ticks = Math.max(calculated, tick);
int stopIndex = (int) (ticks & mask);
HashedWheelBucket bucket = wheel[stopIndex];
bucket.addTimeout(timeout);
}
}
}
|
最后看下到期任务的执行部分源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
public void expireTimeouts(long deadline) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = head;
while (timeout != null) {
HashedWheelTimeout next = timeout.next;
if (timeout.remainingRounds <= 0) {
next = remove(timeout);
if (timeout.deadline <= deadline) {
timeout.expire();
}
} else if (timeout.isCancelled()) {
next = remove(timeout);
} else {
timeout.remainingRounds --;
}
timeout = next;
}
}
|
以上就是相关的原理分析,如有错误欢迎指正

