我们在使用Spring开发的时候,可能有的时候不小心就会写出来循环依赖,但是大部分情况下都能正常运行,不需要我们特别关注,这是因为Spring进行了相关的处理等
循环依赖的处理还依赖于bean的作用范围,bean的注入方式等,这里我们就以单例模式,属性注入的方式来分析一下Spring对于循环依赖的处理
我们以如下场景为例来进行分析,有ServiceA和ServiceB两个Bean, 它们互相依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Service
public class ServiceA {
@Resource
private ServiceB serviceB;
}
@Service
public class ServiceB {
@Resource
private ServiceA serviceA;
}
|
先说结论,然后再进行操作和分析,spring的创建过程大致如下
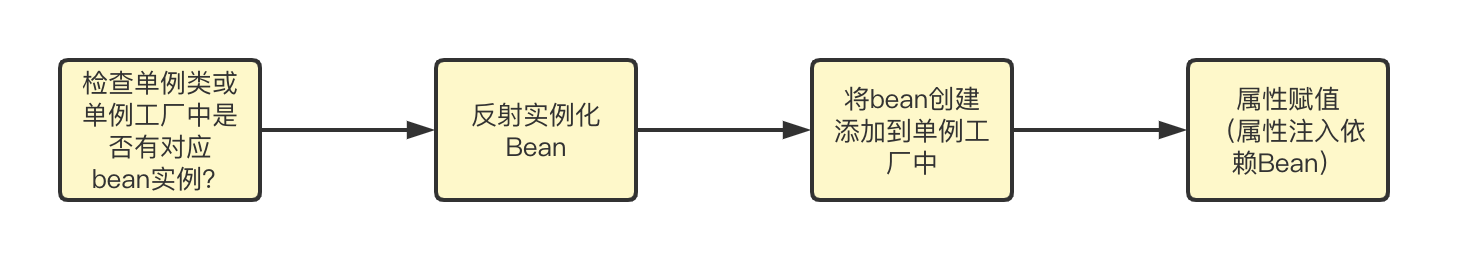
处理循环依赖的关键就是其中的注册单例Bean工厂(singletonFactories)相关功能
- 首次获取ServiceA这个bean时,单例工厂中不存在,这时候会进行实例化并将结果添加到bean工厂中
- 处理ServiceA中属性注入的ServiceB,这时候会从bean工厂中获取ServiceB的bean
- 单例工厂中不存在的ServiceB, 这时候会进行实例化ServiceB并将结果添加到bean工厂中
- 处理ServiceB中属性注入的ServiceA,这时候会从bean工厂中获取ServiceA的bean
- 发现单例工厂中存在ServiceA对应的工厂,从工厂获取bean返回,ServiceB中属性注入完成
- SeriveA中属性注入完成,循环依赖处理完成
源码分析
因为之前已经初步分析过Bean的创建过程,所以这次我们只关注相关的代码,针对上述过程看一下源码
Bean获取过程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
protected <T> T doGetBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType, Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
}
public Object getSingleton(String beanName) {
return getSingleton(beanName, true);
}
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
|
Bean创建过程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
}
return exposedObject;
}
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}
|
Bean中属性注入依赖处理
这里需要提一下,Bean中属性注入的依赖,是由以下两个BeanPostProcessor来分别进行处理的
org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理@Resource)
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理@Autowired)
处理底层是一样的,这次我们就以CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor为例进行分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
}
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
}
return pvs;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
public void inject(Object target, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
if (this.isField) {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
else {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
try {
Method method = (Method) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
|
getResourceToInject会调用到CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.ResourceElement中的对应方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| protected Object getResourceToInject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {
return (this.lazyLookup ? buildLazyResourceProxy(this, requestingBeanName) :
getResource(this, requestingBeanName));
}
protected Object getResource(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LookupElement element, String requestingBeanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
return autowireResource(this.resourceFactory, element, requestingBeanName);
}
protected Object autowireResource(BeanFactory factory, CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LookupElement element, String requestingBeanName)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
Object resource;
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames;
String name = element.name;
if (this.fallbackToDefaultTypeMatch && element.isDefaultName &&
factory instanceof AutowireCapableBeanFactory && !factory.containsBean(name)) {
}
else {
resource = factory.getBean(name, element.lookupType);
autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);
}
return resource;
}
|
以上就是一个简单的循环依赖处理过程
